Jaloka Therapy in Ayurveda and its Practical Application
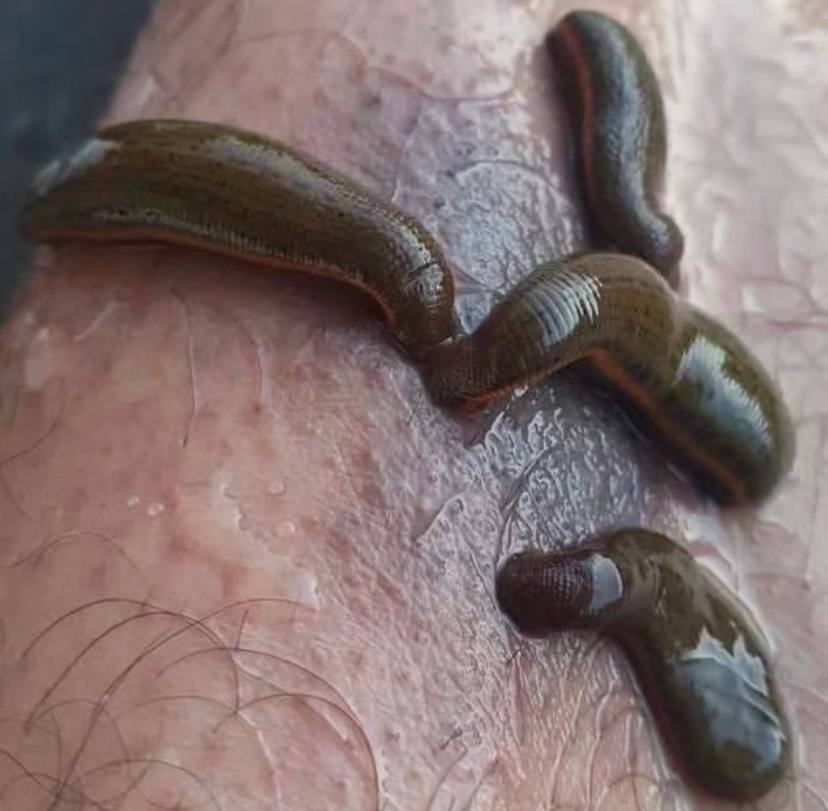
Jaloka, also known as leech therapy, is an ancient therapeutic practise based on Ayurveda, the traditional Indian medical system. This one-of-a-kind treatment involves applying medicinal leeches to the body in order to promote healing and balance. Due to its potential benefits in a variety of medical conditions, the practise has gained renewed interest in recent years. In this article, we will look at the principles, historical context, and practical aspects of Ayurvedic Jaloka therapy. Historical context: Jaloka therapy has been practised for thousands of years and is mentioned in classic Ayurvedic texts such as the Charaka Samhita and the Sushruta Samhita. These texts describe the therapeutic use of leeches to treat ailments caused by imbalanced doshas (Vata, Pitta, and Kapha) and to aid in bloodletting for a variety of conditions. The therapy was especially popular for treating disorders associated with excess Pitta dosha and blood stagnation. Jaloka Therapy Concepts: The use of leeches is based on Ayurvedic principles of dosha balance and circulation enhancement. Leeches’ saliva contains enzymes with anticoagulant, anti-inflammatory, and analgesic properties. When leeches attach to the skin and begin feeding, these enzymes are secreted into the bloodstream, aiding in the reduction of blood stagnation, inflammation, and pain. The therapy is thought to cleanse the blood, remove toxins, and rebalance the body’s vital energies. Practical Application: Before beginning Jaloka therapy, a thorough examination of the patient’s constitution, doshic imbalances, and the specific condition is required. A qualified Ayurvedic practitioner will determine whether the therapy is appropriate for the individual. Medicinal leeches are carefully selected based on their size, health, and suitability for the patient. Only a few species of leeches are used for medicinal purposes. The skin of the patient is cleansed and prepared for leech application. Warm water soaks may be advised to dilate blood vessels and facilitate leech attachment. Leeches are applied to specific points on the body, which often correspond to Ayurvedic marma points (vital energy points). Leeches attach themselves to the skin and begin feeding. The patient is closely monitored throughout the therapy for any adverse reactions or excessive bleeding. When the leeches are full, they are allowed to detach on their own. Following the detachment of the leeches, the wounds are cleaned and dressed. To aid in the healing process, patients are advised to follow a specific diet and lifestyle recommendations. Jaloka Therapy is used to treat the following conditions: Jaloka therapy has traditionally been used to treat a variety of conditions, including: Psoriasis, eczema, and vitiligo are examples of skin disorders. Arthritis and joint pain are two examples of musculoskeletal problems. Varicose veins and thrombosis are examples of circulatory disorders. Certain eye and ear conditions. Conditions characterised by localised congestion and inflammation. Precautions and Modern Relevance: While Jaloka therapy has withstood the test of time, its modern application necessitates careful thought. To prevent infections, proper hygiene and sterilisation are critical. People who have bleeding disorders, weakened immune systems, or a history of allergies should avoid this therapy. Before undergoing Jaloka therapy, it is critical to seek the advice of a qualified Ayurvedic practitioner. Conclusion: Jaloka therapy is a testament to Ayurveda’s holistic healing approach, which encompasses the balance of physical, mental, and spiritual well-being. Its practical application necessitates expertise, adherence to safety precautions, and knowledge of the individual’s unique constitution. As interest in traditional healing practises grows, Jaloka therapy provides an intriguing glimpse into Ayurvedic wisdom and its potential to complement modern medical approaches.
Jaloka Therapy in Ayurveda and its Practical Application Read More »